5.6 KiB
ssd1306: Introduction
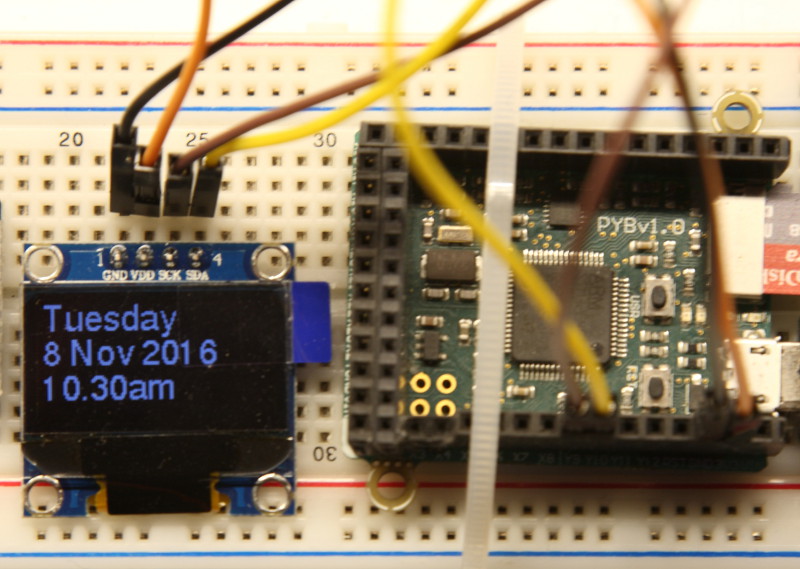
The official SSD1306 OLED display driver supports a single 8x8 pixel monospaced
font. Users of the 128x64 displays in particular may wish to use larger fonts.
This provides a means of extending the official driver to support this. Suitable
font files may be created from standard ttf or otf files using the utility
presented here.
Requires firmware dated 1st Dec 2017 or later.
A few users have pointed out limitations in the Writer class. While it works
it is a rather minimal "proof of concept" for the font creator. PR's offering
enhancements will be gratefully considered.
The font file format is something of a "given" as it is used elsewhere. So any PR requiring this to be changed is unlikely to find favour.
Main README
Release notes
V0.21 21st March 2017 The Writer class now uses the framebuf blit method.
This works for monochrome devices using 1-bit colour mapping. Example code is
provided for rendering to colour devices: the framebuf class does not yet offer
an effective way to handle colour mapping when blitting between buffers with
differing colour maps.
Note that framebuf scrolling does not clear the exposed region of the screen. This is by design but see issue #2692.
Files
- ssd1306_test.py A simple test program.
- ssd1306.py A snapshot of the current official driver.
- writer.py A generic Writer class. Keeps track of the text insertion point over multiple fonts, handles newline and vertical scrolling if required.
In addition several font files are provided as samples.
Getting started
The file ssd1306_test.py may need editing to match your hardware notably
the values of WIDTH and HEIGHT which are set to 128x64 (w*h) pixels. Wiring
details are included in code comments but may be changed if required as soft
I2C and SPI interfaces are specified.
Its principal testing was performed on Pyboards but I'd expect it to be
portable to any device supporting the official driver and the machine module.
Copy files 1-3 and freesans20.py to the target and issue
import ssd1306_test
ssd1306_test.test() # If it uses an I2C connection
ssd1306_test.test(True) # If it uses SPI
Principle of Operation
Font files are converted to Python modules for ease of use and also (optionally) to enable the modules to be frozen as bytecode to reduce RAM requirements.
The user program should import all fonts which are to be used and declare a
Writer instance for each one. Rendering text at the current insertion point
is then simply a matter of issuing the appropriate writer's printstring
method. After issuing all such calls required by your application the display
should be updated by issuing
ssd.show()
The Writer class
The principal interaction with the driver is via this class. One instance should
be created for each font in use. Its function is to keep track of the text
insertion point over successive uses with multiple fonts and to handle newline
characters and vertical scrolling. Its behaviour when text overruns the end of
a line or the bottom of the screen may be controlled using its set_clip
method.
Methods
ConstructorThis takes thessddisplay instance and the font module as mandatory args.printstringTakes a text string as argument and renders it at the current insertion point. Respects newline characters.
Class methods
set_textposMandatory integer argsrow,coldefined in pixels relative to the top left hand corner of the display. Sets the current text insertion point. The coordinates of a glyph refer to its top left corner. The initial default is (0,0) with text being rendered at the top left of the display.set_clipMandatory boolean argsrow_clip,col_clip. These define behaviour when text overruns the physical width or height of the display. By default text overrunning the display width will continue on the next row. Settingcol_clipoverrides this such that overrunning text is lost. Similarly, by default text overrunning the bottom of the display will cause text above to scroll up to accommodate it. Settingrow_clipwill override this behaviour causing text to be clipped.
Use of font_to_py.py
To convert font files to Python for use with this driver the default (vertical)
mapping and bit order should be used. The only optional argument which may be
needed is -f if fixed-width rendering is desired.
License
Any code placed here is released under the MIT License (MIT).
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2016 Peter Hinch
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.